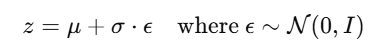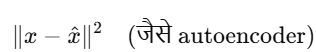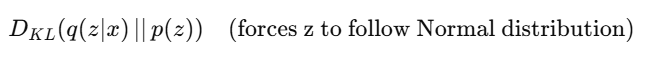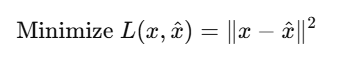अब हम Autoencoders के दो प्रायोगिक उपयोगों (applications) को विस्तार से समझेंगे —
🔹 Denoising
🔹 Dimensionality Reduction
ये दोनों real-world problems में बहुत उपयोगी हैं और deep learning की शक्ति को बख़ूबी दर्शाते हैं।
🔶 1. Application 1: Denoising Autoencoder
❓ What is it?
Denoising Autoencoder (DAE) एक ऐसा Autoencoder है जो noisy input को clean output में बदलना सीखता है।
🎯 “Input को जानबूझकर corrupt किया जाता है और model को सिखाया जाता है कि वह clean version reconstruct करे।”
📦 Working:
Original Image (x)
↓ Add Noise
Noisy Input (x̃)
↓
[Encoder + Decoder]
↓
Clean Output (x̂)
Model learns to minimize:
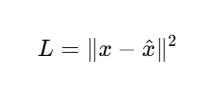
🔧 Example in PyTorch:
def add_noise(imgs, noise_factor=0.3):
noisy_imgs = imgs + noise_factor * torch.randn_like(imgs)
return torch.clip(noisy_imgs, 0., 1.)
You then train autoencoder with (noisy_img, original_img) pairs.
🧠 Use Cases:
| Use | Description |
|---|---|
| 🖼️ Image Denoising | Remove noise from pictures |
| 📄 Document Cleanup | Clean scanned papers |
| 📢 Audio Denoising | Remove background noise |
| 🧠 Medical | Remove sensor noise in ECG, MRI, etc. |
🔶 2. Application 2: Dimensionality Reduction
❓ What is it?
Autoencoder compresses high-dimensional data into a low-dimensional latent representation, similar to PCA (Principal Component Analysis) — but with non-linear capabilities.
🎯 “Autoencoder = Non-linear, trainable PCA”
📦 Example:
| Input | 784-dim vector (28×28 image)
| Encoder | Reduces it to 2D or 3D latent code
| Decoder | Reconstructs full image
| Output | Use latent codes for clustering, visualization, etc.
🔧 PyTorch Sketch:
# Encoder output is just 2D
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(784, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 2) # 2D Latent Space
)
🧠 Use Cases:
| Use | Description |
|---|---|
| 📊 Data Visualization | Compress to 2D for t-SNE / plots |
| 🔍 Clustering | Group similar inputs (e.g., digits, faces) |
| ⚡ Fast Inference | Work on lower-dimensional features |
| 📈 Feature Extraction | Use compressed codes for ML models |
| 🎮 Game AI | Compress game states |
📝 Practice Questions:
- Denoising Autoencoder क्या है और कैसे काम करता है?
- Noise हटाने के लिए Autoencoder को कैसे train किया जाता है?
- Dimensionality reduction में Autoencoder और PCA में क्या अंतर है?
- Latent space का क्या role है?
- Low-dimensional representation किन real-world problems में काम आता है?
📌 Summary
| Application | Input | Output | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Denoising | Noisy image | Clean image | Noise removal |
| Dimensionality Reduction | High-dim data | Low-dim features | Visualization, clustering, compression |