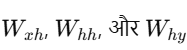Transfer Learning के अंदर दो मुख्य तरीके होते हैं:
👉 Feature Extraction
👉 Fine-Tuning
आइए इन दोनों को विस्तार से समझते हैं — ताकि आप सही स्थिति में सही तरीका चुन सकें।
🔶 1. Feature Extraction क्या होता है?
Feature Extraction का अर्थ है कि हम एक pre-trained model के शुरूआती layers (convolution या transformer blocks) को freeze कर देते हैं और उन्हें features extractor की तरह उपयोग करते हैं।
📌 केवल final classification layer को नए data पर train किया जाता है।
✅ Use when:
- आपके पास कम training data है
- Pre-trained features आपके नए task के लिए पर्याप्त हैं
- Model को जल्दी train करना है
🧱 Example:
from torchvision import models
import torch.nn as nn
model = models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
# Freeze all convolution layers
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
# Replace final classification layer
model.fc = nn.Linear(model.fc.in_features, 2)
🔶 2. Fine-Tuning क्या होता है?
Fine-Tuning में हम pre-trained model के कुछ या सभी layers को unfreeze करते हैं और उन्हें भी re-train करते हैं — ताकि वे नए task के अनुसार adjust हो सकें।
📌 यह तरीका अधिक compute-intensive है लेकिन अक्सर बेहतर results देता है।
✅ Use when:
- आपके पास अधिक training data है
- New task original task से काफ़ी अलग है
- आप high accuracy चाहते हैं
🧱 Example:
# Unfreeze last few layers only (optional)
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if "layer4" in name or "fc" in name:
param.requires_grad = True
else:
param.requires_grad = False
🔁 3. तुलना: Feature Extraction vs Fine-Tuning
| Feature | Feature Extraction | Fine-Tuning |
|---|---|---|
| Layers Frozen | सभी convolutional layers | कुछ या सभी layers train होते हैं |
| Train Time | तेज़ | धीरे |
| Data Requirement | कम | अधिक |
| Flexibility | सीमित | उच्च |
| Performance (accuracy) | ठीक | बेहतर (especially for complex tasks) |
| जब उपयोग करें | Data कम हो, similar task | Data अधिक हो, अलग task हो |
🧠 Visual Diagram:
[Pretrained Model]
↓
┌─────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐
│ Conv Layers │ ───► │ Classifier │ → Output
└─────────────┘ └───────────────┘
↑ ↑
| └─ Trained (Fine-tuning)
└─ Frozen (Feature Extraction)
📝 Practice Questions:
- Feature extraction और fine-tuning में क्या अंतर है?
- Feature extraction कब उपयोग करना चाहिए?
- Fine-tuning को कब avoid करना चाहिए?
- PyTorch में किसी model के कौन से layers freeze/unfreeze होते हैं, कैसे देखें?
- कौन-सी technique ज्यादा computation मांगती है?
🎯 Summary
| Point | Feature Extraction | Fine-Tuning |
|---|---|---|
| Training Layers | केवल classifier | कुछ या सभी layers |
| Data Need | कम | ज़्यादा |
| Accuracy | Moderate | Better |
| Computation | Low | High |
| Flexibility | Low | High |