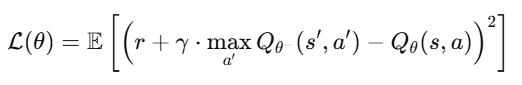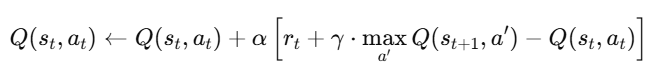ब हम Natural Language Processing (NLP) का एक बहुत ही महत्वपूर्ण विषय सीखते हैं —
🧠 Word Embeddings, जो deep learning-based NLP की नींव रखते हैं।
🔶 1. Word Embeddings क्या हैं?
Word Embeddings वो तकनीक है जिससे शब्दों को संख्याओं (vectors) में represent किया जाता है — इस तरह कि उनके semantic (meaningful) रिश्ते भी capture हों।
🎯 “Word Embeddings words को mathematical space में ऐसे map करते हैं कि उनके बीच के अर्थ संबंध भी साफ़ दिखें।”
🧠 क्यों ज़रूरी हैं?
Traditional NLP methods जैसे One-Hot Encoding सिर्फ पहचानते हैं कि कोई शब्द है या नहीं — लेकिन वो शब्दों के अर्थ या संबंध को नहीं समझते।
| Technique | समस्या |
|---|---|
| One-Hot | High dimensional, sparse, no meaning |
| Embedding | Dense, low-dimensional, meaningful representation |
📏 2. Embedding Vector कैसा होता है?
Word → Vector (जैसे 300 dimensions का dense vector):
| Word | Vector (छोटा version) |
|---|---|
| king | [0.25, 0.67, …, 0.12] |
| queen | [0.23, 0.65, …, 0.14] |
| banana | [0.10, 0.32, …, 0.91] |
| democracy | [0.55, 0.40, …, 0.60] |
👉 Words जो अर्थ में करीब होते हैं, उनके vectors भी पास होते हैं।
📊 3. Word2Vec
🧪 Developed By:
Google (2013) — Tomas Mikolov et al.
⚙️ Idea:
- शब्दों के context के आधार पर embedding सीखना।
- “You shall know a word by the company it keeps.”
🔁 Two Architectures:
| Architecture | कार्य |
|---|---|
| CBOW (Continuous Bag of Words) | Nearby words से center word predict करता है |
| Skip-Gram | Center word से आसपास के words predict करता है |
🔍 Word2Vec Diagram:
[The] [king] [of] [Spain] → [rules]
↑ context → target
CBOW: Predict “rules”
Skip-Gram: Predict “The”, “king”, “Spain” ← “rules”
🧠 4. GloVe (Global Vectors)
🧪 Developed By:
Stanford (2014) — Jeffrey Pennington et al.
⚙️ Idea:
- Word2Vec local context पर निर्भर करता है
- GloVe पूरे corpus के co-occurrence matrix का उपयोग करता है
🧾 Objective:
Find word vectors so that:
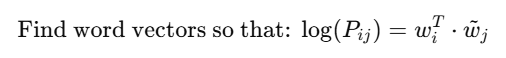
जहाँ Pij दो शब्दों के co-occurrence का ratio है।
🔍 Word2Vec vs GloVe
| Aspect | Word2Vec | GloVe |
|---|---|---|
| Context | Local window | Global corpus statistics |
| Type | Predictive | Count-based |
| Training | Faster | Slower (matrix-based) |
| Accuracy | High | Slightly better for analogies |
| Use Case | Fast semantic learning | Fine-grained vector space |
🧪 5. Real Example: Word Analogy
king−man+woman≈queen
Word Embeddings में ये relation mathematically मिल जाता है! 🔥
🧰 6. Python Example (Gensim – Word2Vec)
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
sentences = [["I", "love", "deep", "learning"],
["Word2Vec", "captures", "semantic", "meaning"]]
model = Word2Vec(sentences, vector_size=50, window=2, min_count=1, sg=1)
print(model.wv["deep"]) # Embedding vector
print(model.wv.most_similar("learning"))
📌 7. Pretrained Embedding Sources
| Embedding | Source |
|---|---|
| GloVe | https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/ |
| Word2Vec | https://code.google.com/archive/p/word2vec/ |
| FastText | https://fasttext.cc/ |
| BERT Embeddings | HuggingFace (transformers library) |
📈 8. Applications
| Use Case | How Embeddings Help |
|---|---|
| 🗣️ Chatbots | Words with similar meanings treated similarly |
| 📝 Sentiment Analysis | “bad” vs “awful” को पहचानना |
| 🔁 Translation | Semantic similarity across languages |
| 💬 Q&A Systems | Understanding user intent |
📝 Practice Questions:
- Word Embeddings क्या होते हैं?
- Word2Vec के दो architecture कौन-कौन से हैं?
- GloVe और Word2Vec में मुख्य अंतर बताइए।
- एक embedding vector की structure को समझाइए।
- Word analogy कैसे काम करता है embedding space में?
🧠 Summary Table
| Topic | Summary |
|---|---|
| Word Embedding | Words → meaningful vectors |
| Word2Vec | Learns from local context (CBOW, Skip-gram) |
| GloVe | Learns from global co-occurrence |
| Advantage | Semantic similarity capture करना |
| Application | Chatbots, translation, classification |