अब हम एक और महत्वपूर्ण और रोचक deep learning तकनीक को समझेंगे —
📦 Autoencoder
जिसका उपयोग representation learning, dimensionality reduction, और unsupervised learning में होता है।
🔶 1. Definition (परिभाषा):
Autoencoder एक ऐसा neural network है जिसे input को ही output के रूप में reproduce करने के लिए train किया जाता है — लेकिन इस प्रक्रिया में यह data के compressed और meaningful features सीखता है।
🎯 “Autoencoder खुद से feature सीखता है — बिना किसी label के।”
🧠 2. Structure of Autoencoder
Autoencoder में तीन मुख्य भाग होते हैं:
- Encoder: Input को compress करता है (latent space में)
- Latent Space: Data का compressed representation
- Decoder: Compressed data को reconstruct करता है
Diagram:
Input
↓
[Encoder]
↓
Compressed Code (Latent Vector)
↓
[Decoder]
↓
Reconstructed Output
🧮 3. Objective (Loss Function)
Autoencoder को train करने का उद्देश्य है:
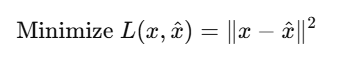
जहाँ:
- x: Original input
- x^: Reconstructed output
- L: Mean Squared Error (या कोई और loss)
🧱 4. Types of Autoencoders
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| 🔹 Vanilla Autoencoder | Basic encoder-decoder structure |
| 🔹 Sparse Autoencoder | Regularization to learn sparse codes |
| 🔹 Denoising Autoencoder | Noisy input → Clean reconstruction |
| 🔹 Variational Autoencoder (VAE) | Probabilistic latent space |
| 🔹 Convolutional Autoencoder | CNN-based encoder-decoder for images |
🔧 5. PyTorch Example (Basic Autoencoder)
import torch.nn as nn
class Autoencoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Autoencoder, self).__init__()
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(784, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 32),
)
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(32, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 784),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.encoder(x)
x = self.decoder(x)
return x
📊 6. Applications of Autoencoders
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| ✅ Dimensionality Reduction | जैसे PCA से बेहतर |
| ✅ Image Denoising | Noise हटाना |
| ✅ Anomaly Detection | Outlier data पकड़ना |
| ✅ Data Compression | Latent representation |
| ✅ Image Colorization | Black & white → Color |
| ✅ Feature Extraction | For downstream tasks |
🔄 7. Difference from PCA
| PCA | Autoencoder |
|---|---|
| Linear | Non-linear |
| No training | Trained via gradient descent |
| Limited capacity | Learn complex structure |
| Fixed basis | Flexible learned features |
📝 Practice Questions:
- Autoencoder क्या होता है?
- Autoencoder में latent space का क्या महत्व है?
- Vanilla और Denoising Autoencoder में क्या अंतर है?
- Autoencoder का loss function क्या होता है?
- Autoencoder का प्रयोग कहाँ किया जा सकता है?
🎯 Summary
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Input = Output | Learns to reconstruct data |
| Unsupervised | कोई label नहीं चाहिए |
| Encoder + Decoder | Compress और reconstruct करता है |
| Applications | Compression, denoising, anomaly detection |


