अब हम deep learning की सबसे आधुनिक और प्रभावशाली तकनीकों में से एक को सीखने जा रहे हैं — जो text-to-image जैसे tasks में breakthroughs लाई है:
🔍 धीरे-धीरे noise जोड़ो, फिर धीरे-धीरे उसे हटाकर नया data generate करो!
🔷 1. What are Diffusion Models?
Diffusion Models एक तरह के generative models हैं, जो training में images में noise डालते हैं और फिर सीखते हैं उसे वापस original image में बदलना।
🧠 Goal: Noise से high-quality image generate करना।
🔶 2. Real World Analogy
कल्पना कीजिए आपके पास एक साफ़ तस्वीर है, जिसे आप बार-बार थोड़ा-थोड़ा धुंधला (noise) करते हैं। अब model सीखता है कि कैसे इस धुंधली तस्वीर से साफ़ तस्वीर वापस बनाई जाए।
🔷 3. Core Idea
Diffusion Process में दो चरण होते हैं:
✅ 1. Forward Process (Adding Noise)
Original image में step-by-step Gaussian noise मिलाया जाता है।
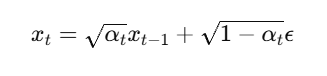
- जहां
x_0= original image x_t= noisy image at step tε= Gaussian noise
✅ 2. Reverse Process (Denoising)
Model सीखता है कि इस noise को step-by-step हटाकर original image कैसे reconstruct की जाए।
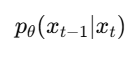
🔶 4. Intuition:
| Stage | क्या हो रहा है |
|---|---|
| Forward Process | Image → Noise |
| Reverse Process | Noise → Image (generate करने के लिए!) |
🔷 5. Architecture
Diffusion models आमतौर पर U-Net architecture का उपयोग करते हैं।
- Noise-added image input किया जाता है
- Time-step embedding दिया जाता है
- U-Net output करता है predicted noise
- Loss: MSE between actual noise और predicted noise
🔶 6. Training Objective
Model को सिखाया जाता है:
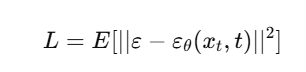
यानी: Model सिखे कि original noise (ε) क्या था, ताकि उसे हटाकर साफ़ image बन सके।
🔷 7. Famous Diffusion Models
| Model | Highlights | Organization |
|---|---|---|
| DDPM | Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model | |
| Stable Diffusion | Text-to-Image diffusion model | Stability AI |
| Imagen | High-quality generation from text | Google Brain |
| DALLE-2 | CLIP + Diffusion | OpenAI |
🔶 8. Applications of Diffusion Models
✅ Text-to-Image Generation
✅ Inpainting (Missing image fill करना)
✅ Super-resolution
✅ Audio synthesis
✅ 3D scene generation
🔷 9. Sample Code (Simplified PyTorch)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class SimpleDenoiseModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(784, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 784),
)
def forward(self, x, t):
return self.net(x)
# Forward diffusion (add noise)
def add_noise(x, t):
noise = torch.randn_like(x)
alpha = 1 - 0.02 * t # Simplified
return alpha * x + (1 - alpha) * noise, noise
🧠 Difference from GANs
| Feature | GAN | Diffusion Model |
|---|---|---|
| Stable | ❌ Hard to train | ✅ More stable |
| Output Quality | Medium to High | ✅ High |
| Mode Collapse | ❌ Possible | ✅ Rare |
| Training Time | Faster | ❌ Slower |
| Use Case | Image, video, text | Mostly high-fidelity images |
📝 Practice Questions:
- Diffusion model में forward और reverse process क्या होते हैं?
- Stable Diffusion किस technique पर आधारित है?
- GAN और Diffusion में क्या अंतर है?
- Time-step embedding क्यों ज़रूरी है?
- Diffusion से कौन-कौन से real-world tasks solve किए जा सकते हैं?
🧾 Summary
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Forward Pass | Clean image → Add noise |
| Reverse Pass | Noisy image → Remove noise (generate) |
| Architecture | Mostly U-Net |
| Training Loss | MSE between true and predicted noise |
| Output | New image generated from pure noise |
