अब हम Autoencoders की एक शक्तिशाली और probabilistic form को समझेंगे —
🔮 Variational Autoencoders (VAE)
जो deep generative models की दुनिया में एक foundation की तरह माने जाते हैं।
🔶 1. What is a Variational Autoencoder?
VAE एक तरह का Autoencoder है, जो ना केवल input को compress करता है,
बल्कि उसे एक probability distribution में encode करता है।
🎯 “VAE compress करता है input को एक distribution के रूप में, जिससे हम new data generate कर सकते हैं।”
🧠 2. Traditional Autoencoder vs VAE
| Feature | Autoencoder | Variational Autoencoder |
|---|---|---|
| Output | Reconstruct input | Reconstruct + Sample new |
| Latent Vector | Fixed values | Probability distribution |
| Generation | No | Yes (Generative model) |
| Learning | Deterministic | Probabilistic |
| Regularization | None | KL Divergence |
🔬 3. VAE Structure
Diagram:
Input x
↓
[Encoder Network]
↓
Latent Distribution (μ, σ)
↓
Sampling (z ~ N(μ, σ))
↓
[Decoder Network]
↓
Reconstructed x̂
🧮 4. Latent Distribution
VAE encoder predicts:
- Mean vector μ
- Log-variance logσ2
From these, we sample latent variable
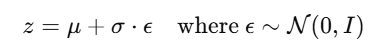
👉 इसे कहते हैं reparameterization trick
ताकि gradient backpropagation संभव हो।
🧮 5. VAE Loss Function
VAE का कुल loss दो हिस्सों से मिलकर बनता है:
L=Reconstruction Loss+ KL Divergence Loss
✅ Reconstruction Loss:
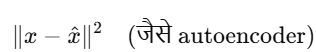
✅ KL Divergence Loss:
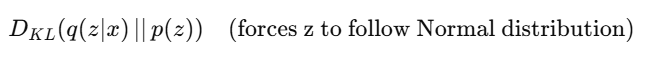
🔧 6. PyTorch Sketch
class VAE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, latent_dim):
super(VAE, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
self.mu = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, latent_dim)
self.log_var = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, latent_dim)
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(latent_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, input_dim),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def encode(self, x):
h = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
return self.mu(h), self.log_var(h)
def reparameterize(self, mu, log_var):
std = torch.exp(0.5 * log_var)
eps = torch.randn_like(std)
return mu + eps * std
def forward(self, x):
mu, log_var = self.encode(x)
z = self.reparameterize(mu, log_var)
return self.decoder(z), mu, log_var
📊 7. Applications of VAE
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| ✅ Image Generation | New samples create करना |
| ✅ Data Imputation | Missing values भरना |
| ✅ Representation Learning | Compressed features |
| ✅ Anomaly Detection | Rare patterns पकड़ना |
| ✅ Drug Design | Molecule generation |
🎨 8. Generated Sample Example (MNIST)
Train VAE on MNIST, then sample new digits by:
z = torch.randn(1, latent_dim)
generated = model.decoder(z)
👉 ऐसा output real handwritten digit जैसा दिखेगा, despite not being in the original dataset.
📝 Practice Questions:
- VAE क्या है और Autoencoder से कैसे अलग है?
- Latent vector के लिए reparameterization क्यों ज़रूरी है?
- VAE का loss function किन भागों में बँटा होता है?
- KL divergence का क्या उद्देश्य होता है?
- VAE से synthetic data कैसे generate किया जाता है?
🎯 Summary
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| VAE | Probabilistic autoencoder |
| Encoder Output | μ और σ (mean & std) |
| Sampling | z = μ + σ * ε |
| Loss | Reconstruction + KL divergence |
| Use Cases | Generation, anomaly detection, compression |
